Precise measurement of intracranial pressure Measurement of ICP (Intracranial Pressure) in the Brain
Intracranial Pressure (ICP) refers to the pressure within the skull, particularly within the brain tissue and cerebrospinal fluid. Elevated ICP can indicate various neurological issues or conditions, potentially leading to severe complications.
Neuromonitoring catheters, like RAUMEDIC's NEUROVENT series, are specialized devices used to measure the ICP. They are inserted into the brain at different measuring locations, allowing direct monitoring of pressure changes. This information is crucial in assessing and managing conditions like traumatic brain injury.
How does the ICP Measurement from RAUMEDIC work?
RAUMEDIC offers numerous possibilities for measuring the intracranial pressure. Depending on the measuring location and indication, the setup and the components can be variably combined.
In the video you can see an exemplary application of parenchymal ICP measurement with the NEUROVENT-P with BOLT CH5 and NPS2.
ICP Measurement Locations in Different Areas of the Brain
ICP (Intracranial Pressure) can be measured in several locations within the brain using specialized neuromonitoring techniques:
A catheter is inserted directly into the brain tissue (parenchyma) to measure the pressure. This is one of the most common methods of ICP measurement. Due to its substantial size as part of the brain, the parenchyma provides favorable options for catheter application, making this technique one possible method that can be employed for measuring Intracranial Pressure (ICP).
A catheter is placed in one of the lateral ventricles, which are fluid-filled spaces. This allows for not only ICP measurement but also the drainage of cerebrospinal fluid if necessary.
Neuromonitoring Catheters for ICP Measurement in the Parenchyma
For precise assessment of pressure directly within the brain tissue during neurointensive treatment, one approach is the measurement with a catheter in the parenchyma. RAUMEDIC offers a wide range of NEUROVENT measurement catheters for measuring intracranial pressure (ICP) in the parenchyma.
NEUROVENT-P
Parenchymal ICP measurement
NEUROVENT-P-TEMP
Parenchymal ICP and temperature (ICT) measurement
NEUROVENT-PTO
Parenchymal ICP, temperature (ICT) and oxygen partial pressure (ptiO2) measurement
NEUROVENT-PTO 2L
Unique catheter to measure ICP, ICT and ptiO2 for the application with a BOLT KIT PTO 2L and a microdialysis catheter.
NEUROVENT Catheters for Ventricular ICP Measurement
RAUMEDIC offers various types of NEUROVENT ventricular catheters for direct measurement of intracranial pressure in the brain’s ventricles or even parenchyma.
NEUROVENT
Ventricular ICP measurement with CSF drainage
NEUROVENT-IFD-S
Ventricular ICP measurement with CSF drainage and soft internal guide wire
NEUROVENT-IFD-R
Ventricular ICP measurement with CSF drainage and rigid internal guide wire
NEUROVENT-TEMP
Ventricular ICP and temperature (ICT) measurement with CSF drainage
NEUROVENT-TEMP-IFD-S
Ventricular ICP and temperature (ICT) measurement with CSF drainage and soft internal guide wire
NEUROVENT-TEMP-IFD-R
Ventricular ICP and temperature (ICT) measurement with CSF drainage and rigid internal guide wire
NEUROVENT-Sleeve Housing
Parenchymal ICP measurement and ventricular CSF drainage
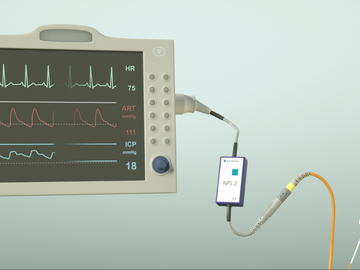
Plug & Play - Patient Monitor Connection with NPS2
The NPS2, or Zero-Point Simulator, by RAUMEDIC ensures Plug & Play integration with patient monitors as part of the measuring chain, enabling access to neuromonitoring data and curves. This system ensures user-friendly handling without the need for manual calibration of measurement catheters.
Comprehensive monitoring solutions
Visualization and storage with MPR2 logO DATALOGGER
Display and storage of measured ICP, ICT and ptiO2.
Display of data with EASY logO
Simple display of ICP, ICT and ptiO2-data, data storage on the patient monitor by transferring the values.
FAQ: Indications of ICP Measurement
Accurate ICP measurement is vital because it provides essential data about the brain's health and helps guide treatment decisions. Elevated ICP can impede blood flow to the brain, potentially leading to tissue damage and worsening of neurological conditions. Timely intervention based on precise ICP measurements is therefore critical for optimizing patient outcomes in neurocritical care.
The limited expansion volume of the skull, due to its rigid structure, means that any increase in volume within the cranium can lead to a rise in Intracranial Pressure (ICP). This is a critical concern because the brain, encased within the skull, has limited space to accommodate any additional volume or pressure. As such, even a slight increase in volume, whether from swelling, bleeding, or other factors, can lead to a significant increase in ICP.
- Craniocerebral injury GCS (<=) 8
- Malignant cerebral infarction
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage Hunt/Hess grade IV + V
- Cerebral oedema
- Hydrocephalus
- Idiopathic intracranial hypertension
- Macrocephaly
- Any increase in ICP